Metal Finishing: Processes, Techniques, and Applications
Sep 4 ,2025
Metal Surface finishing is a critical step in the production of metal components. A quality metal surface treatment improves both the appearance and functionality of completed components, making parts look better and, crucially, last longer. This comprehensive guide explores the various metal finishing processes, their benefits, and applications.
What is Metal Finishing?
Metal finishing refers to a variety of treatments or processes that range from polishing to techniques that affect a metal’s molecular structure. It includes cleaning treatments, polishing methods, and other operations designed to improve and enhance the surface of metal products.
Why is Metal Finishing Important?
Metal finishing extends the suitability of metals, allowing cheaper metals to be used in place of more expensive ones. Finishing processes can improve electrical conductivity, durability, chemical resistance, and corrosion protection. Additionally, finishing enhances aesthetic quality, creating uniform surfaces desired in consumer products.
Types of Metal Finishing Processes
1. Plating (Electroplating and Electroless Plating)
Metal plating involves covering a substrate with thin layers of another metal such as zinc, nickel, chromium, or cadmium. This process improves durability, surface friction, corrosion resistance, and appearance.
2. Anodizing
An electrochemical process that creates a long-lasting, attractive, and corrosion-resistant anodic oxide finish. Most commonly used for aluminum parts but effective on nonferrous metals like magnesium and titanium.
3. Metal Grinding
Uses abrasives to smooth metal surfaces and decrease surface roughness left from previous machining processes. Various grinders are available including surface grinders, Blanchard grinders, and centerless grinders.
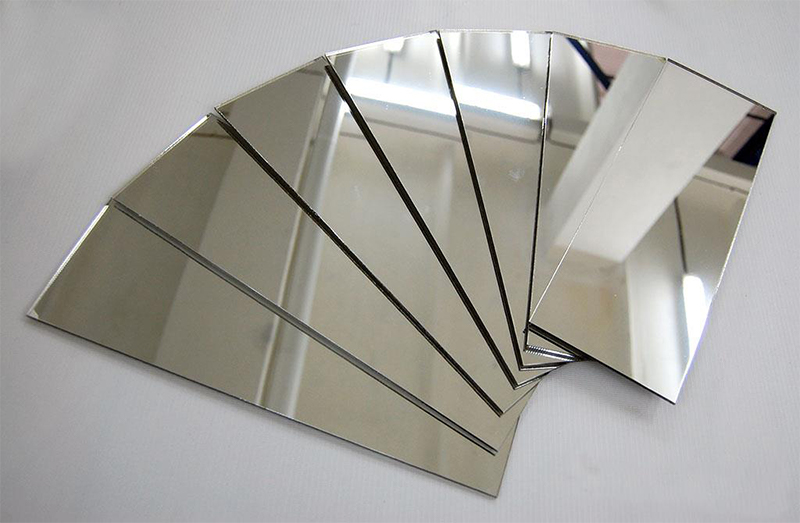
4. Polishing/Buffing
Employs abrasive materials with felt or leather wheels to reduce surface roughness and improve appearance. Also used to create hygienic vessels and components in certain industries.
5. Electropolishing
The inverse of electroplating, this process removes metal ions from the surface rather than depositing them. Results in a polished, smooth surface free of flaws, rust, and dirt.
6. Painting and Powder Coating
Painting adds color and prevents corrosion, while powder coating uses electrostatic charge to attach powder particles to metal parts before heat treatment. Both offer cost-effective finishing options.
7. Blasting
Abrasive blasting creates a consistent matte texture while cleaning and finishing in a single operation. Uses high-pressure abrasive flow to modify texture and remove debris.
8. Brushing
Uses abrasive belts and tools to create a uniform surface texture with directional grain. Recommended for corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
Metal Finishing Techniques Comparison
| Process | Primary Benefits | Best For | Cost Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electroplating | Corrosion resistance, improved appearance | Decorative items, automotive parts | Moderate to high |
| Anodizing | Durability, corrosion resistance | Aluminum components | Moderate |
| Powder Coating | Color options, durability | Consumer products, automotive parts | Low to moderate |
| Polishing/Buffing | Aesthetic improvement, hygienic surfaces | Medical equipment, decorative items | Varies (labor-intensive) |
| Blasting | Surface cleaning, uniform texture | Preparation for other finishes | Low |
Choosing the Right Metal Finishing Process
Selecting the appropriate finishing method requires considering several factors:
- Level of finish required
- Base metal type
- Time constraints
- Preparation work needed
- Budget limitations
- End product specifications
Applications of Metal Finishing
Almost every metal component used in industrial settings or sold as part of consumer products incorporates some level of surface finishing. Applications include:
- Automotive components
- Aerospace parts
- Medical devices and equipment
- Consumer electronics
- Architectural elements
- Industrial machinery
Benefits and Drawbacks of Metal Finishing
Advantages:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance
- Improved aesthetic quality
- Increased durability and wear resistance
- Better electrical conductivity (in some processes)
- Ability to use cheaper base materials
Disadvantages:
- Increased production costs
- Extended production time
- Additional handling requirements
- Potential limitations on operating conditions (e.g., temperature constraints with certain paints)
Conclusion
Surface finishing is critical in the manufacturing of metal products, providing benefits to both end users and manufacturers. The appropriate finishing technique depends on the product specifications, base material, and budget constraints. Understanding both the limitations of metal finishing processes and the requirements of the final product is essential for achieving optimal results. From electroplating to powder coating, each method offers unique advantages that can enhance the functionality, durability, and appearance of metal components across various industries.